
What is Die Casting Molds and How Do They Work?
Die Casting Molds play a crucial role in manufacturing. These molds shape molten metal into complex parts efficiently. According to John Smith, a leading expert in the die casting industry, "The precision of die casting molds determines the quality of the final product." This emphasizes their importance.
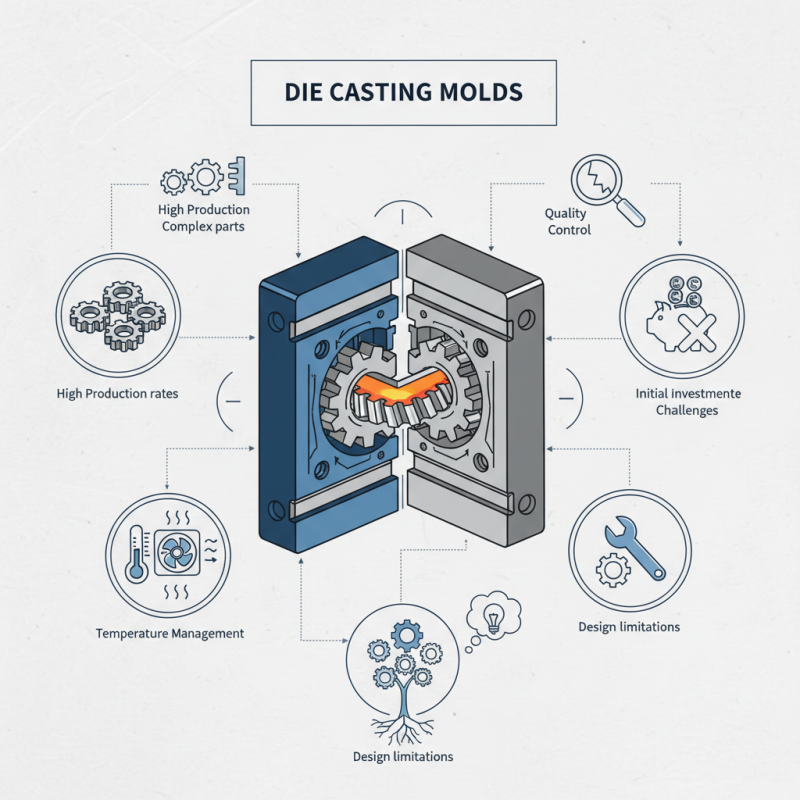
Die casting molds consist of two halves. They can create intricate designs with high accuracy. The process allows high production rates. However, the initial investment is significant, and maintaining quality can be challenging. Managing temperature is critical. If not done correctly, defects may arise.
Understanding die casting molds requires recognizing their limitations. Not all designs are suitable for die casting. Complex shapes can lead to issues. Manufacturers need to evaluate their options carefully. Continuous advancements in technology create both opportunities and challenges. It is essential to reflect on the process to achieve the best results.
What Are Die Casting Molds?
Die casting molds are essential tools used in the manufacturing process. They are designed to create precise metal parts through the injection of molten metal into molds. The process allows for mass production of complex shapes with minimal waste. According to a recent report, the global die casting market is projected to reach over $10 billion by 2025, highlighting the demand for efficient manufacturing solutions.
These molds are typically made from steel or iron, and their construction can be quite intricate. A well-designed mold ensures uniform cooling and reduces defects. However, the initial cost of creating a quality die casting mold can be high. It requires careful planning and precision engineering. In many cases, molds have a lifespan that can be compromised if not maintained properly. Industry insights indicate that mold failure can lead to production delays and increased costs.
Despite these challenges, die casting molds have significant advantages. They allow for high-volume production and excellent dimensional accuracy. Many manufacturers report a reduction in post-production machining due to the precision achieved during casting. However, issues like air entrapment can still occur, affecting the final product. As the industry evolves, continuous improvement in mold design and materials is crucial.
The Materials Used in Die Casting Molds
Die casting molds are crucial in manufacturing. They shape molten metal into specific forms. The materials used for these molds are vital for durability and efficiency.
Typically, steel is the primary choice due to its strength. Tool steel is even better, handling high temperatures and pressure. Aluminum molds are lighter but less durable, making them suitable for lower production runs. Some manufacturers explore zinc alloys for smaller parts. They offer excellent fluidity in casting.
Considering material costs is essential. High-quality molds can be expensive. But, cheap materials might lead to defects. It's a balancing act. Experimenting with combinations can sometimes yield surprising results. This process isn't always perfect. There will be failures along the way, each offering a lesson on what to improve next time. Finding the right material remains a challenge but is necessary for successful die casting.
The Die Casting Process Explained Step-by-Step
Die casting is a vital manufacturing process. It uses molten metal to create precise shapes. Understanding the die casting process can help improve production efficiency.
The die casting process starts with mold preparation. Molds are typically made from tool steel or other durable materials. Next, molten metal is poured into the mold at high pressure. This pressure forces the metal to fill every intricate detail of the mold. Cooling follows, where the metal solidifies into the desired shape. Finally, the mold opens to release the finished part. According to industry reports, die casting can achieve tolerances as tight as ±0.1 mm, ensuring high precision.
Tips: Choosing the right mold material is crucial for durability. Steel molds, although more expensive, last longer and withstand high temperatures. Keep in mind that maintaining molds is essential. Regular checks can prevent defects and extend their lifespan.
One common challenge in die casting is managing thermal expansion. Metals expand when heated, which can lead to imperfections. Companies often overlook this issue, resulting in wasted materials and time. Proper thermal management can mitigate such risks and enhance overall quality.
What is Die Casting Molds and How Do They Work? - The Die Casting Process Explained Step-by-Step
| Step | Description | Materials Used | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Preparation of Mold | Steel, Aluminum | Automotive Parts |
| 2 | Melting the Metal | Zinc, Magnesium | Consumer Electronics |
| 3 | Injection of Metal into Mold | Aluminum Alloys | Industrial Machinery |
| 4 | Cooling and Solidification | - | Aerospace Components |
| 5 | Ejection of Casting from Mold | - | Construction Equipment |
| 6 | Finishing Process | Paints, Coatings | Home Appliances |
Types of Die Casting Molds and Their Applications
Die casting molds are essential tools in manufacturing. They allow for the creation of complex metal parts with precision. There are several types of die casting molds, each serving different purposes. Hot chamber molds are usually for low-melting metals, while cold chamber molds work well for high-temperature alloys. Each mold type presents its own challenges.
Tooling is crucial; an improper design can lead to defects. For example, thick walls may create uneven cooling. This affects the final product's integrity. Moreover, the cost of creating molds can be high. However, investing in quality molds often pays off in durability and output. A well-designed mold can generate thousands of parts consistently.
Applications for die casting molds are vast. They are used in automobiles, electronics, and appliances. Each industry requires specific features. For example, an automotive part needs to withstand pressure. This demands precise mold specifications. Yet, many manufacturers overlook the significance of testing molds before mass production. Evaluating the designs could save time and resources later.
Maintenance and Care for Die Casting Molds
Maintaining die casting molds is crucial for quality production. Molds must be cleaned regularly to prevent residue build-up. This residue can affect the final product. Use soft materials to avoid scratching the mold surface. Lubrication is essential too. A proper lubricant prevents wear and tear during operations.
Inspecting molds often is a part of routine maintenance. Look for signs of wear, such as cracks or warping. These imperfections, if neglected, can lead to costly mistakes. Frequent checks help in addressing issues before they escalate. Proper storage of molds is equally important. Store them in a dry environment to avoid corrosion.
Over time, some molds may require repair or replacement. It’s a good practice to document any maintenance work. Keeping a log helps in analyzing patterns. This can assist in making informed decisions about future investments. Remember, taking care of die casting molds today saves time and resources tomorrow.
Die Casting Mold Maintenance Frequency
This bar chart illustrates the frequency of maintenance sessions performed on die casting molds over a year. Regular maintenance ensures optimal performance and longevity of the molds, with the highest frequency of sessions occurring monthly.


