
What is Plastic Injection Mold and How Does it Work?
Plastic Injection Molding is a fascinating manufacturing technique. It transforms raw plastic material into various shapes. This process involves melting plastic pellets and injecting them into a mold. Once cooled, they take on the mold's form.
The importance of a plastic injection mold cannot be overstated. It defines the final shape and finish of the product. Intricate designs can be achieved, thanks to precise molds. However, designing a mold is not always straightforward. There are challenges, such as costs and time constraints.
Many overlook the complexities of this process. While it may seem simple, each step requires careful planning. Even minor mistakes can lead to defects. Understanding these nuances is essential for a successful outcome. The value of a well-designed plastic injection mold lies in its ability to produce consistent, high-quality items efficiently.
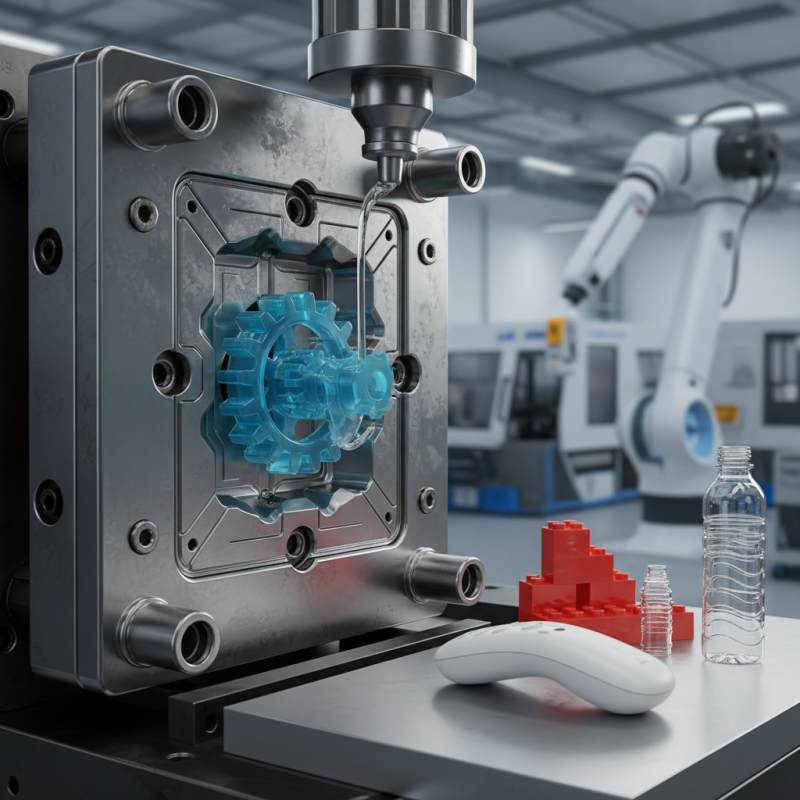
What is Plastic Injection Molding?
Plastic injection molding is a manufacturing process used in various industries. This method involves injecting molten plastic into a mold to create parts and products. The versatility of plastic injection molding makes it widely utilized. According to a report by MarketsandMarkets, the global plastic injection molding market is projected to reach $410 billion by 2026.
The process starts with a hopper, where plastic pellets are fed. These pellets are heated until they become liquid. The liquid plastic is then injected into a pre-shaped mold under high pressure. Once cooled, the mold opens, and the finished part is ejected. The cycle time can vary from a few seconds to minutes, determined by part geometry and size. Many industries rely on this process, including automotive, consumer goods, and electronics.
Despite its advantages, challenges remain. Designing an efficient mold can be expensive. Small design flaws can impact the product quality significantly. Moreover, the environmental concerns surrounding plastic usage cannot be ignored. Recycling options are limited, and the production process emits greenhouse gases. Thus, continuous improvement in both technology and sustainability practices is essential moving forward.
What is Plastic Injection Mold and How Does it Work?
| Dimension | Description |
|---|---|
| Definition | Plastic injection molding is a manufacturing process for producing parts by injecting molten material into a mold. |
| Applications | Used in various industries including automotive, consumer goods, electronics, and medical devices. |
| Materials Used | Common materials include thermoplastics, thermosetting plastics, and elastomers. |
| Process Steps | 1. Material is melted. 2. Injected into the mold. 3. Cooled and solidified. 4. Ejected from the mold. |
| Advantages | High precision, efficient production, and ability to produce complex shapes. |
| Challenges | High initial cost of molds and design considerations for part removal. |
| Cycle Time | Typically ranges from 15 seconds to several minutes depending on part size and complexity. |
Key Components of a Plastic Injection Mold
Plastic injection molds are intricate tools used to shape plastic materials. Understanding the key components is essential for grasping how these molds function. One vital element is the cavity, which determines the final shape of the product. The design of the cavity significantly impacts the flow of plastic and the quality of the final part. It requires precision and careful planning, as any flaw can lead to production defects.
Another important component is the core, which works in tandem with the cavity. The core forms the inner details of the molded part. Its alignment with the cavity must be perfect, or issues will arise. Often, the cooling channels are overlooked. These channels help remove heat from the mold. Inadequate cooling can cause warping. It's a common issue in the industry. Many designs fail to consider adequate airflow, leading to longer production cycles.
The ejection system is crucial for removing the finished product from the mold. If not designed properly, it can cause damage to the part. Operators often face challenges with ejection force and timing. Errors can lead to increased wear on the mold, requiring costly repairs. Here, attention to detail is paramount. Balancing these components can be tricky, but it is essential for producing high-quality plastic parts.
Plastic Injection Mold Usage by Industry
The Injection Molding Process Steps Explained
The injection molding process is crucial in manufacturing plastic parts. It begins with creating a mold, typically from steel or aluminum. This mold is engineered for durability and precision. According to a report by Grand View Research, the global market for injection molding is projected to reach $307 billion by 2025.
Once the mold is ready, thermoplastic pellets are heated until they melt. This molten plastic is then injected into the mold under high pressure. It fills the cavity completely, ensuring that every detail is captured. After a brief cooling period, the mold opens, and the part is ejected. Proper cooling is essential; too fast can lead to warping, while too slow can slow production.
Throughout this process, monitoring quality is vital. As noted in a study by MarketsandMarkets, defects can arise from poor mold design or improper material selection. Ensuring a consistent temperature and pressure is critical. Anomalies can result in waste and increased costs. As the industry grows, continuous improvements in molding technology must address these challenges.
Materials Used in Plastic Injection Molding
Plastic injection molding is a widely used manufacturing process. It relies heavily on the choice of materials. Popular options include thermoplastics and thermosetting plastics. These materials are chosen for their versatility and ability to form intricate designs.
Thermoplastics, such as polyethylene and polystyrene, are often used. They can be reheated and reshaped. This characteristic makes them a cost-effective choice for many applications. Thermosetting plastics, like epoxy, are also important. Once set, they cannot be remolded. This makes them suitable for items that need strong structural integrity.
Choosing the right material is crucial. Different applications require different properties. Not all plastics are suitable for every project. Some may not withstand heat or chemicals. It's essential to test materials before full production. Manufacturers must consider their specific needs to avoid costly mistakes. Testing can reveal unexpected issues, leading to reflections on design choices.
Applications and Benefits of Plastic Injection Molding
Plastic injection molding is a widely used manufacturing process. It creates parts by injecting molten plastic into a mold. This method offers substantial advantages across various industries. According to a report by the American Injection Molding Industry, production costs can drop by over 50% when using injection molding compared to traditional methods.
The applications of plastic injection molding are vast. It’s essential in automotive, medical, and consumer goods sectors. For instance, lightweight vehicle components reduce fuel consumption. Medical devices, made using precise molds, ensure patient safety. In consumer goods, the process enables mass production of intricate designs efficiently. However, waste material remains an issue, with some studies suggesting up to 15% excess plastic in production. Reducing this waste is critical for sustainability goals.
Efficiency is another crucial benefit. The cycle time can be as short as 15 seconds, allowing high-volume production. However, achieving high-quality parts consistently can be challenging. Minor errors in mold design can lead to defects. Companies must invest in rigorous testing and quality control. This vigilance is essential to maintain alignment with industry standards and meet customer demands.


